#Step-by-Step GitLab guide
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
GitLab CI CD Pipelines for Home Lab: A Step-by-Step Guide
GitLab CI CD Pipelines for Home Lab: A Step-by-Step Guide #homelab #selfhosted #GitLabCICDtutorial #HomeLabCICDsetup #StepByStepGitLabguide #CICDPipelinesexplained #GitLabhomelabprojects #ContinuousDeploymentHomeLab #ContinuousIntegration#GitLabPipeline
If you are like me, for years, you have used scheduled tasks in the home lab and production to accomplish various tasks. However, delving into the world of CI CD opens many opportunities to learn how to use this instead of rudimentary scheduled tasks to carry out automation. And the benefits are tremendous, especially when you use source to manage your DevOps code. However, many see the term “ci…

View On WordPress
#CI/CD Home Lab Tips#CI/CD Pipelines explained#Continuous Deployment Home Lab#Continuous Integration Guide#GitLab CI/CD tutorial#GitLab home lab projects#GitLab Pipelines walkthrough#Home Lab CI/CD setup#Master GitLab Pipelines#Step-by-Step GitLab guide
0 notes
Text

Welcome back, coding enthusiasts! Today we'll talk about Git & Github , the must-know duo for any modern developer. Whether you're just starting out or need a refresher, this guide will walk you through everything from setup to intermediate-level use. Let’s jump in!
What is Git?
Git is a version control system. It helps you as a developer:
Track changes in your codebase, so if anything breaks, you can go back to a previous version. (Trust me, this happens more often than you’d think!)
Collaborate with others : whether you're working on a team project or contributing to an open-source repo, Git helps manage multiple versions of a project.
In short, Git allows you to work smarter, not harder. Developers who aren't familiar with the basics of Git? Let’s just say they’re missing a key tool in their toolkit.
What is Github ?
GitHub is a web-based platform that uses Git for version control and collaboration. It provides an interface to manage your repositories, track bugs, request new features, and much more. Think of it as a place where your Git repositories live, and where real teamwork happens. You can collaborate, share your code, and contribute to other projects, all while keeping everything well-organized.
Git & Github : not the same thing !
Git is the tool you use to create repositories and manage code on your local machine while GitHub is the platform where you host those repositories and collaborate with others. You can also host Git repositories on other platforms like GitLab and BitBucket, but GitHub is the most popular.
Installing Git (Windows, Linux, and macOS Users)
You can go ahead and download Git for your platform from (git-scm.com)
Using Git
You can use Git either through the command line (Terminal) or through a GUI. However, as a developer, it’s highly recommended to learn the terminal approach. Why? Because it’s more efficient, and understanding the commands will give you a better grasp of how Git works under the hood.
GitWorkflow
Git operates in several key areas:
Working directory (on your local machine)
Staging area (where changes are prepared to be committed)
Local repository (stored in the hidden .git directory in your project)
Remote repository (the version of the project stored on GitHub or other hosting platforms)
Let’s look at the basic commands that move code between these areas:
git init: Initializes a Git repository in your project directory, creating the .git folder.
git add: Adds your files to the staging area, where they’re prepared for committing.
git commit: Commits your staged files to your local repository.
git log: Shows the history of commits.
git push: Pushes your changes to the remote repository (like GitHub).
git pull: Pulls changes from the remote repository into your working directory.
git clone: Clones a remote repository to your local machine, maintaining the connection to the remote repo.
Branching and merging
When working in a team, it’s important to never mess up the main branch (often called master or main). This is the core of your project, and it's essential to keep it stable.
To do this, we branch out for new features or bug fixes. This way, you can make changes without affecting the main project until you’re ready to merge. Only merge your work back into the main branch once you're confident that it’s ready to go.
Getting Started: From Installation to Intermediate
Now, let’s go step-by-step through the process of using Git and GitHub from installation to pushing your first project.
Configuring Git
After installing Git, you’ll need to tell Git your name and email. This helps Git keep track of who made each change. To do this, run:

Master vs. Main Branch
By default, Git used to name the default branch master, but GitHub switched it to main for inclusivity reasons. To avoid confusion, check your default branch:

Pushing Changes to GitHub
Let’s go through an example of pushing your changes to GitHub.
First, initialize Git in your project directory:

Then to get the ‘untracked files’ , the files that we haven’t added yet to our staging area , we run the command

Now that you’ve guessed it we’re gonna run the git add command , you can add your files individually by running git add name or all at once like I did here

And finally it's time to commit our file to the local repository

Now, create a new repository on GitHub (it’s easy , just follow these instructions along with me)
Assuming you already created your github account you’ll go to this link and change username by your actual username : https://github.com/username?tab=repositories , then follow these instructions :


You can add a name and choose wether you repo can be public or private for now and forget about everything else for now.

Once your repository created on github , you’ll get this :

As you might’ve noticed, we’ve already run all these commands , all what’s left for us to do is to push our files from our local repository to our remote repository , so let’s go ahead and do that

And just like this we have successfully pushed our files to the remote repository
Here, you can see the default branch main, the total number of branches, your latest commit message along with how long ago it was made, and the number of commits you've made on that branch.

Now what is a Readme file ?
A README file is a markdown file where you can add any relevant information about your code or the specific functionality in a particular branch—since each branch can have its own README.
It also serves as a guide for anyone who clones your repository, showing them exactly how to use it.
You can add a README from this button:

Or, you can create it using a command and push it manually:

But for the sake of demonstrating how to pull content from a remote repository, we’re going with the first option:

Once that’s done, it gets added to the repository just like any other file—with a commit message and timestamp.
However, the README file isn’t on my local machine yet, so I’ll run the git pull command:

Now everything is up to date. And this is just the tiniest example of how you can pull content from your remote repository.
What is .gitignore file ?
Sometimes, you don’t want to push everything to GitHub—especially sensitive files like environment variables or API keys. These shouldn’t be shared publicly. In fact, GitHub might even send you a warning email if you do:

To avoid this, you should create a .gitignore file, like this:

Any file listed in .gitignore will not be pushed to GitHub. So you’re all set!
Cloning
When you want to copy a GitHub repository to your local machine (aka "clone" it), you have two main options:
Clone using HTTPS: This is the most straightforward method. You just copy the HTTPS link from GitHub and run:

It's simple, doesn’t require extra setup, and works well for most users. But each time you push or pull, GitHub may ask for your username and password (or personal access token if you've enabled 2FA).
But if you wanna clone using ssh , you’ll need to know a bit more about ssh keys , so let’s talk about that.
Clone using SSH (Secure Shell): This method uses SSH keys for authentication. Once set up, it’s more secure and doesn't prompt you for credentials every time. Here's how it works:
So what is an SSH key, actually?
Think of SSH keys as a digital handshake between your computer and GitHub.
Your computer generates a key pair:
A private key (stored safely on your machine)
A public key (shared with GitHub)
When you try to access GitHub via SSH, GitHub checks if the public key you've registered matches the private key on your machine.
If they match, you're in — no password prompts needed.
Steps to set up SSH with GitHub:
Generate your SSH key:

2. Start the SSH agent and add your key:

3. Copy your public key:

Then copy the output to your clipboard.
Add it to your GitHub account:
Go to GitHub → Settings → SSH and GPG keys
Click New SSH key
Paste your public key and save.
5. Now you'll be able to clone using SSH like this:

From now on, any interaction with GitHub over SSH will just work — no password typing, just smooth encrypted magic.
And there you have it ! Until next time — happy coding, and may your merges always be conflict-free! ✨👩💻👨💻
#code#codeblr#css#html#javascript#java development company#python#studyblr#progblr#programming#comp sci#web design#web developers#web development#website design#webdev#website#tech#html css#learn to code#github
93 notes
·
View notes
Text
DevOps for Beginners: Navigating the Learning Landscape
DevOps, a revolutionary approach in the software industry, bridges the gap between development and operations by emphasizing collaboration and automation. For beginners, entering the world of DevOps might seem like a daunting task, but it doesn't have to be. In this blog, we'll provide you with a step-by-step guide to learn DevOps, from understanding its core philosophy to gaining hands-on experience with essential tools and cloud platforms. By the end of this journey, you'll be well on your way to mastering the art of DevOps.

The Beginner's Path to DevOps Mastery:
1. Grasp the DevOps Philosophy:
Start with the Basics: DevOps is more than just a set of tools; it's a cultural shift in how software development and IT operations work together. Begin your journey by understanding the fundamental principles of DevOps, which include collaboration, automation, and delivering value to customers.
2. Get to Know Key DevOps Tools:
Version Control: One of the first steps in DevOps is learning about version control systems like Git. These tools help you track changes in code, collaborate with team members, and manage code repositories effectively.
Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD): Dive into CI/CD tools like Jenkins and GitLab CI. These tools automate the building and deployment of software, ensuring a smooth and efficient development pipeline.
Configuration Management: Gain proficiency in configuration management tools such as Ansible, Puppet, or Chef. These tools automate server provisioning and configuration, allowing for consistent and reliable infrastructure management.
Containerization and Orchestration: Explore containerization using Docker and container orchestration with Kubernetes. These technologies are integral to managing and scaling applications in a DevOps environment.
3. Learn Scripting and Coding:
Scripting Languages: DevOps engineers often use scripting languages such as Python, Ruby, or Bash to automate tasks and configure systems. Learning the basics of one or more of these languages is crucial.
Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Delve into Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tools like Terraform or AWS CloudFormation. IaC allows you to define and provision infrastructure using code, streamlining resource management.
4. Build Skills in Cloud Services:
Cloud Platforms: Learn about the main cloud providers, such as AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud. Discover the creation, configuration, and management of cloud resources. These skills are essential as DevOps often involves deploying and managing applications in the cloud.
DevOps in the Cloud: Explore how DevOps practices can be applied within a cloud environment. Utilize services like AWS Elastic Beanstalk or Azure DevOps for automated application deployments, scaling, and management.
5. Gain Hands-On Experience:
Personal Projects: Put your knowledge to the test by working on personal projects. Create a small web application, set up a CI/CD pipeline for it, or automate server configurations. Hands-on practice is invaluable for gaining real-world experience.
Open Source Contributions: Participate in open source DevOps initiatives. Collaborating with experienced professionals and contributing to real-world projects can accelerate your learning and provide insights into industry best practices.
6. Enroll in DevOps Courses:
Structured Learning: Consider enrolling in DevOps courses or training programs to ensure a structured learning experience. Institutions like ACTE Technologies offer comprehensive DevOps training programs designed to provide hands-on experience and real-world examples. These courses cater to beginners and advanced learners, ensuring you acquire practical skills in DevOps.

In your quest to master the art of DevOps, structured training can be a game-changer. ACTE Technologies, a renowned training institution, offers comprehensive DevOps training programs that cater to learners at all levels. Whether you're starting from scratch or enhancing your existing skills, ACTE Technologies can guide you efficiently and effectively in your DevOps journey. DevOps is a transformative approach in the world of software development, and it's accessible to beginners with the right roadmap. By understanding its core philosophy, exploring key tools, gaining hands-on experience, and considering structured training, you can embark on a rewarding journey to master DevOps and become an invaluable asset in the tech industry.
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Unlocking Full-Stack Development: A Comprehensive Roadmap for Aspiring Developers in India
In the era of digital transformation, the demand for skilled full-stack developers in India is soaring. These versatile professionals proficient in both frontend and backend development are essential for building dynamic web applications. If you're aspiring to become a full-stack developer in India, this comprehensive roadmap will guide you through the steps to achieve your goal.

1. Grasp the Essentials of Web Development: To kickstart your journey as a full-stack developer, begin by mastering the core concepts of web development. Dive into HTML, CSS, and JavaScript—the fundamental languages for creating web pages. Understanding these basics lays a solid foundation for your future endeavors.
2. Select a Backend Language and Framework: Once you're comfortable with frontend technologies, delve into backend development by choosing a programming language and framework. Options like Python with Django, JavaScript with Node.js, or Ruby with Ruby on Rails are popular choices. These backend technologies empower you to handle server-side logic and data management efficiently.
3. Acquire Proficiency in Database Management: Database management is a critical aspect of full-stack development. Familiarize yourself with database systems such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, or MongoDB. Learn database querying, indexing, and normalization to effectively store and retrieve data for your web applications.
4. Explore Frontend Frameworks and Libraries: Enhance your frontend development skills by mastering popular frameworks and libraries. React.js, Angular, and Vue.js are widely used for building dynamic user interfaces. Dive deep into these tools to create interactive components and manage application state seamlessly.
5. Embrace Version Control Systems: Version control is indispensable for collaborative software development. Get hands-on experience with Git and platforms like GitHub or GitLab. Learn to create repositories, commit changes, and collaborate with other developers to streamline your workflow.
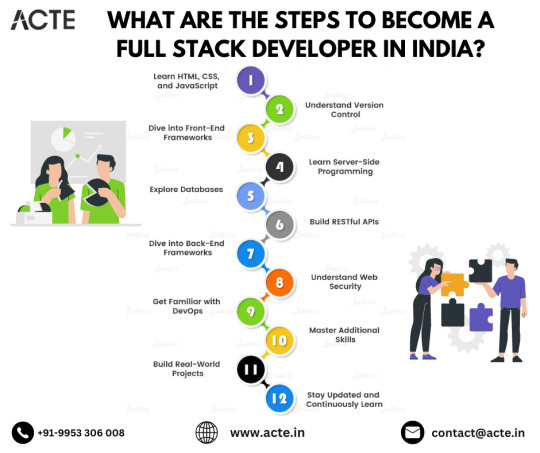
6. Sharpen Your Problem-Solving Skills: Problem-solving is a core competency for any developer. Practice solving coding challenges and algorithms on platforms such as LeetCode, HackerRank, or CodeSignal. Strengthening your problem-solving abilities will prepare you for technical interviews and real-world coding scenarios.
7. Develop Projects and Build a Portfolio: Apply your knowledge by working on diverse projects that showcase your full-stack development skills. Start with simple projects and gradually tackle more complex ones to demonstrate your proficiency. Create a portfolio website to exhibit your projects, expertise, and accomplishments to potential employers.
8. Stay Abreast of Industry Trends: The tech landscape evolves rapidly, so it's crucial to stay updated with the latest trends and technologies. Attend tech meetups, workshops, and conferences to network with industry professionals and learn from their experiences. Follow influential blogs, podcasts, and social media channels to stay informed about emerging trends and best practices.
9. Pursue Internship Opportunities: Internships provide invaluable hands-on experience and exposure to real-world projects. Look for internship opportunities at companies or startups where you can apply your skills in a professional environment. Internships also offer opportunities for mentorship and networking, which can be invaluable for your career growth.
10. Cultivate a Continuous Learning Mindset: Becoming a full-stack developer is a journey of lifelong learning and growth. Stay curious, explore new technologies, and continuously expand your skill set. Be open to adapting to new challenges and opportunities as they arise, and embrace a growth mindset to thrive in the ever-evolving tech industry.
Conclusion: Mastering full-stack development in India requires dedication, perseverance, and a commitment to lifelong learning. By following this comprehensive roadmap, you can acquire the skills and knowledge needed to excel in this dynamic and rewarding field. So, roll up your sleeves, embark on your full-stack development journey, and unlock a world of endless possibilities in India's thriving tech ecosystem.
#full stack developer#information#education#front end development#full stack web development#full stack developer course#frameworks#backend#technology#web development
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Navigating the DevOps Landscape: A Beginner's Comprehensive
Roadmap In the dynamic realm of software development, the DevOps methodology stands out as a transformative force, fostering collaboration, automation, and continuous enhancement. For newcomers eager to immerse themselves in this revolutionary culture, this all-encompassing guide presents the essential steps to initiate your DevOps expedition.

Grasping the Essence of DevOps Culture: DevOps transcends mere tool usage; it embodies a cultural transformation that prioritizes collaboration and communication between development and operations teams. Begin by comprehending the fundamental principles of collaboration, automation, and continuous improvement.
Immerse Yourself in DevOps Literature: Kickstart your journey by delving into indispensable DevOps literature. "The Phoenix Project" by Gene Kim, Jez Humble, and Kevin Behr, along with "The DevOps Handbook," provides invaluable insights into the theoretical underpinnings and practical implementations of DevOps.
Online Courses and Tutorials: Harness the educational potential of online platforms like Coursera, edX, and Udacity. Seek courses covering pivotal DevOps tools such as Git, Jenkins, Docker, and Kubernetes. These courses will furnish you with a robust comprehension of the tools and processes integral to the DevOps terrain.
Practical Application: While theory is crucial, hands-on experience is paramount. Establish your own development environment and embark on practical projects. Implement version control, construct CI/CD pipelines, and deploy applications to acquire firsthand experience in applying DevOps principles.

Explore the Realm of Configuration Management: Configuration management is a pivotal facet of DevOps. Familiarize yourself with tools like Ansible, Puppet, or Chef, which automate infrastructure provisioning and configuration, ensuring uniformity across diverse environments.
Containerization and Orchestration: Delve into the universe of containerization with Docker and orchestration with Kubernetes. Containers provide uniformity across diverse environments, while orchestration tools automate the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications.
Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD): Integral to DevOps is CI/CD. Gain proficiency in Jenkins, Travis CI, or GitLab CI to automate code change testing and deployment. These tools enhance the speed and reliability of the release cycle, a central objective in DevOps methodologies.
Grasp Networking and Security Fundamentals: Expand your knowledge to encompass networking and security basics relevant to DevOps. Comprehend how security integrates into the DevOps pipeline, embracing the principles of DevSecOps. Gain insights into infrastructure security and secure coding practices to ensure robust DevOps implementations.
Embarking on a DevOps expedition demands a comprehensive strategy that amalgamates theoretical understanding with hands-on experience. By grasping the cultural shift, exploring key literature, and mastering essential tools, you are well-positioned to evolve into a proficient DevOps practitioner, contributing to the triumph of contemporary software development.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Unleashing Creativity: Teaching Web Development Basics
Gaining a foundational understanding of web development is becoming just as important for students as traditional education in this age of digital innovation. Students’ creativity is stimulated and they are prepared for a world in which having an online presence is crucial by being introduced to HTML, CSS, and fundamental web design concepts.

Here are some methods teachers can use:
Project-Based Learning: Plan experiential learning opportunities that walk students through building a simple website. Introduce CSS for styling gradually after starting with basic HTML structures.
Platform: Use online platforms like CodePen, Glitch, or Repl.it to provide a real-time coding environment. These platforms allow students to see instant visual results as they code.
Interactive Tutorials: Introduce interactive tutorials that guide students through the basics of HTML and CSS. Platforms like Codecademy or freeCodeCamp offer step-by-step lessons with immediate feedback.
Platform: Codecademy, freeCodeCamp, and Khan Academy are excellent platforms for interactive tutorials, allowing students to learn at their own pace.
Collaborative Coding: Encourage your students to collaborate on projects during collaborative coding sessions. This encourages collaboration and facilitates peer learning among students.
Platform: Utilize version control systems like GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket. These platforms enable students to collaborate on code, manage versions, and receive feedback from peers and teachers.
Web Development Bootcamps: Introduce mini “BOOTCAMP” sessions where students immerse themselves in intensive, focused learning for a short period. Cover key HTML and CSS concepts during these sessions.
Platform: Platforms like Udacity, Coursera, or edX offer short-term courses and bootcamps on web development that can be adapted for classroom use.
Showcasing Web Design Principles: Teach not just the coding but also the principles of good web design. Discuss topics like user experience (UX) and user interface (UI) design.

Throughout your classes, provide fascinating information about web development. For example, did you know that the very first website ever made is still up and running? Being able to share these trivia not only makes learning more enjoyable but also piques students’ interests.
For kids, adding a foundational understanding of web programming to upper-grade courses opens up a world of opportunities. Makers’ Muse Ed-Tech provides the materials and tools required to make learning successful and interesting. Teachers may spark students’ interest in technology and equip them to become the next generation of digital landscape creators by teaching HTML, CSS, and fundamental web design principles. Together with Makers’ Muse, let’s educators take our students on this fascinating adventure that will cultivate their creativity and provide them with the tools they need to succeed in the rapidly changing field of web development.
#html#css#web development#web design#web developers#artificial intelligence#coding#education#coding for kids#future#innovation#tech#coding course#programming#digital world#tumbler#tumblog
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Freelance Web Development Useful Tricks
In today’s digital age, businesses and individuals are constantly seeking professional help to build and maintain their online presence. This surge in demand has paved the way for a booming market in freelance web development. Whether you're a seasoned Freelance Web Developer or just stepping into the world of freelance work, learning a few practical tricks can significantly improve your productivity, client relationships, and project outcomes.
This guide provides useful tips and insights tailored for those working as a Freelance Web Designer, Web Developer Singapore, or a Freelance Website Developer Singapore.
1. Define Your Niche
As a Freelance Web Designer, the first step to building a successful career is finding your niche. Instead of trying to serve everyone, focus on a specific market. For example, becoming a Freelance Website Designer Singapore who specializes in e-commerce platforms can help you attract targeted clients.
Narrowing your services helps you become an expert in that area, making it easier to deliver higher-quality results and command better rates.
2. Build a Professional Portfolio
Your portfolio is your most powerful marketing tool. As a Freelance Web Developer Singapore, it's important to showcase not just finished websites but also the thought process behind them. Include case studies, user experience improvements, and before/after examples.
Clients in web design Singapore often prefer seeing real-world applications. A well-crafted portfolio tells them you are the right Website Designer Singapore for the job.
3. Use Contracts for Every Project
A common mistake new freelancers make is working without a contract. A good contract outlines the project scope, deadlines, payment terms, and revision limits. Whether you’re a Freelance Website Designer or Freelance Web Developer, having a legal agreement helps protect both parties and sets clear expectations.
Especially in regions like Singapore, where business professionalism is crucial, this step adds to your credibility.
4. Embrace Web Design Tools
Leveraging the right tools can save hours of work. Platforms like Figma, Sketch, and Adobe XD are essential for any Freelance Web Designer Singapore. Similarly, GitHub and GitLab are invaluable for version control if you're a Freelance Website Developer.
These tools not only streamline your workflow but also make collaboration easier with clients and teams.
5. Master Responsive Design
Clients expect websites to look perfect on all devices. Mastering responsive design is critical for any Web Developer Singapore. Use flexible grids, images, and CSS media queries to ensure that your designs look and function well on desktops, tablets, and smartphones.
This is especially important in Singapore, where mobile usage is among the highest in the world.
6. Optimize for SEO
A beautiful website is of little use if it can't be found online. Every Freelance Website Designer and Freelance Web Developer Singapore should have a working knowledge of SEO fundamentals. This includes optimizing page speed, using semantic HTML, and ensuring that websites are mobile-friendly.
Clients looking for web design Singapore services often prefer professionals who can provide both design and SEO support.
7. Keep Up With Trends
The web design and development industry is always evolving. Trends like dark mode, voice search optimization, and minimalistic design are shaping the future. As a Freelance Web Designer, staying updated helps you offer modern and appealing designs to your clients.
Being knowledgeable about trends makes you a more competitive Website Developer Singapore or Freelance Website Designer Singapore.
8. Communicate Clearly and Frequently
Good communication is the backbone of freelance success. Regular updates, clear explanations, and managing client expectations are crucial. If you're a Freelance Website Developer in Singapore, effective communication can help you stand out in a market known for its high standards.
Always confirm client needs and follow up with written summaries after meetings.
9. Time Management is Key
Freelancing gives you flexibility, but it also requires discipline. Use project management tools like Trello, Asana, or Notion to organize tasks and deadlines. A Freelance Website Developer Singapore handling multiple clients will benefit greatly from scheduling tools and time tracking apps.
Meeting deadlines consistently will build your reputation as a reliable Website Designer Singapore.
10. Offer Maintenance Services
Many clients need ongoing support after a website goes live. Offering maintenance packages—such as updates, backups, and minor tweaks—is a smart way for any Freelance Web Developer to earn recurring revenue.
In the competitive web design Singapore industry, providing post-launch support can give you an edge over others.
11. Leverage Social Proof
Gather testimonials from satisfied clients and display them prominently on your website. As a Freelance Web Designer Singapore, social proof builds trust and credibility. Encourage clients to leave reviews on platforms like Google, LinkedIn, or Clutch.
It helps potential clients feel more confident in hiring you as their Website Developer Singapore.
12. Price Your Services Smartly
Pricing can make or break a freelance career. Research market rates and consider the complexity of the project before quoting. Whether you're a Freelance Web Developer Singapore or Freelance Website Designer, avoid underpricing just to get a job—it can hurt your business in the long run.
Offer tiered pricing packages to give clients options that match their budget.
13. Network Within the Local Community
Even in a digital world, word-of-mouth still matters. Attend local meetups, seminars, and webinars related to web design Singapore. Building relationships with other professionals can lead to referrals and collaborations.
Being known in the local scene can greatly benefit a Freelance Web Developer Singapore or Freelance Website Developer Singapore.
14. Invest in Learning
Technology changes fast. Take time to learn new frameworks, design patterns, or CMS platforms like WordPress, Webflow, or Shopify. This is especially useful for a Freelance Website Designer Singapore targeting clients in different industries.
Courses from Udemy, Coursera, or free resources like MDN Web Docs can help you stay ahead.
15. Protect Your Work
Always keep backups and secure your source code. Use version control systems and cloud storage to ensure that no data is lost. As a Freelance Website Developer, protecting your work is as important as creating it.
For those in Singapore, where clients expect high data integrity and privacy, security is a must-have skill.
16. Build a Personal Brand
Branding isn’t just for big businesses. As a Freelance Web Designer Singapore, having a personal brand can help you stand out. Use consistent colors, a unique logo, and a professional tone across your website and social profiles.
Your brand is your identity—make it memorable.
17. Specialize in CMS Platforms
Many small businesses prefer using content management systems for easy updates. Specializing in WordPress, Joomla, or Drupal can be a game changer for a Freelance Website Developer Singapore.
Offering CMS-based solutions can expand your market reach in web design Singapore.
18. Set Client Boundaries
To avoid burnout, it's essential to set clear boundaries regarding your work hours, communication channels, and project scope. Many Freelance Web Designers fall into the trap of being available 24/7.
Define and communicate your availability upfront.
19. Ask for Referrals
Don’t hesitate to ask satisfied clients to refer you to others. Referrals are one of the best ways to grow your freelance business. A Freelance Web Developer Singapore can benefit immensely from personal recommendations.
Referrals reduce your need for marketing and often lead to higher-quality clients.
20. Stay Consistent
Consistency is key in delivering quality results and growing your business. Whether you’re a Freelance Website Designer Singapore or a Website Developer Singapore, being consistent in your communication, design style, and deadlines will build trust.
It’s this consistency that builds long-term success.
Final Thoughts
Freelance web development can be a highly rewarding career, but it requires dedication, continuous learning, and smart business practices. Whether you’re a Freelance Web Designer, Freelance Website Developer, or Freelance Web Developer Singapore, applying these tricks can help you improve your workflow, increase client satisfaction, and scale your freelance business effectively.
The demand for quality web design Singapore professionals continues to grow. By sharpening your skills and following the best practices, you can stand out as a top-tier Website Designer Singapore or Website Developer Singapore in a competitive market.
Remember, success in freelancing doesn’t happen overnight. But with consistent effort, a strong portfolio, and these practical tips, you’ll be well on your way to becoming a sought-after Freelance Web Designer Singapore.
Visit https://www.freelancewebdesigner.sg to learn on Website development in Singapore.
#freelance web designer singapore#website designer singapore#web design singapore#web designer singapore#website developer singapore#web developer singapore
0 notes
Text
SRE Roadmap: Your Complete Guide to Becoming a Site Reliability Engineer in 2025
In today’s rapidly evolving tech landscape, Site Reliability Engineering (SRE) has become one of the most in-demand roles across industries. As organizations scale and systems become more complex, the need for professionals who can bridge the gap between development and operations is critical. If you’re looking to start or transition into a career in SRE, this comprehensive SRE roadmap will guide you step by step in 2025.

Why Follow an SRE Roadmap?
The field of SRE is broad, encompassing skills from DevOps, software engineering, cloud computing, and system administration. A well-structured SRE roadmap helps you:
Understand what skills are essential at each stage.
Avoid wasting time on non-relevant tools or technologies.
Stay up to date with industry standards and best practices.
Get job-ready with the right certifications and hands-on experience.
SRE Roadmap: Step-by-Step Guide
🔹 Phase 1: Foundation (Beginner Level)
Key Focus Areas:
Linux Fundamentals – Learn the command line, shell scripting, and process management.
Networking Basics – Understand DNS, HTTP/HTTPS, TCP/IP, firewalls, and load balancing.
Version Control – Master Git and GitHub for collaboration.
Programming Languages – Start with Python or Go for scripting and automation tasks.
Tools to Learn:
Git
Visual Studio Code
Postman (for APIs)
Recommended Resources:
"The Linux Command Line" by William Shotts
GitHub Learning Lab
🔹 Phase 2: Core SRE Skills (Intermediate Level)
Key Focus Areas:
Configuration Management – Learn tools like Ansible, Puppet, or Chef.
Containers & Orchestration – Understand Docker and Kubernetes.
CI/CD Pipelines – Use Jenkins, GitLab CI, or GitHub Actions.
Monitoring & Logging – Get familiar with Prometheus, Grafana, ELK Stack, or Datadog.
Cloud Platforms – Gain hands-on experience with AWS, GCP, or Azure.
Certifications to Consider:
AWS Certified SysOps Administrator
Certified Kubernetes Administrator (CKA)
Google Cloud Professional SRE
🔹 Phase 3: Advanced Practices (Expert Level)
Key Focus Areas:
Site Reliability Principles – Learn about SLIs, SLOs, SLAs, and Error Budgets.
Incident Management – Practice runbooks, on-call rotations, and postmortems.
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) – Master Terraform or Pulumi.
Scalability and Resilience Engineering – Understand fault tolerance, redundancy, and chaos engineering.
Tools to Explore:
Terraform
Chaos Monkey (for chaos testing)
PagerDuty / OpsGenie
Real-World Experience Matters
While theory is important, hands-on experience is what truly sets you apart. Here are some tips:
Set up your own Kubernetes cluster.
Contribute to open-source SRE tools.
Create a portfolio of automation scripts and dashboards.
Simulate incidents to test your monitoring setup.
Final Thoughts
Following this SRE roadmap will provide you with a clear and structured path to break into or grow in the field of Site Reliability Engineering. With the right mix of foundational skills, real-world projects, and continuous learning, you'll be ready to take on the challenges of building reliable, scalable systems.
Ready to Get Certified?
Take your next step with our SRE Certification Course and fast-track your career with expert training, real-world projects, and globally recognized credentials.
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
Exploring the Tools and Technologies Behind Full Stack Web Development
In today’s digital age, having a strong online presence is no longer optional—it’s essential. Whether it’s an e-commerce store, a mobile app, or a blog, the foundation behind any successful web product is solid web development. Among the most in-demand areas in this field is full stack web development. If you're curious about how websites are built from the ground up, or you’re planning to step into the world of programming, this guide is for you.
Here, we’ll be exploring the tools and technologies behind full stack web development, and also take a closer look at how training platforms like full stack by TechnoBridge are shaping the developers of tomorrow.
What is Full Stack Web Development?
Full stack web development refers to the development of both front-end (what users see) and back-end (how things work behind the scenes) parts of a web application. A full stack developer is someone who has the skills and knowledge to work on both ends of the system.
This includes:
Creating user interfaces with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript
Managing server-side logic using frameworks like Node.js or Django
Storing and retrieving data from databases such as MongoDB or MySQL
Version control using Git and GitHub
Deploying apps using platforms like Heroku or AWS
It’s an exciting field where you get to build a complete product and not just a part of it. The sense of ownership and creativity in this space is unmatched.
Key Technologies Used in Full Stack Development
Let’s break down the stack into its major components and explore the popular tools and technologies developers use today:
1. Front-End Technologies (Client Side)
These tools create everything the user interacts with:
HTML5: Structure of the web pages
CSS3: Styling and layout
JavaScript: Interactive elements
Frameworks: React.js, Angular, Vue.js – for building dynamic user interfaces
2. Back-End Technologies (Server Side)
These tools handle the logic and database interactions:
Languages: Node.js (JavaScript), Python, Ruby, PHP, Java
Frameworks: Express.js, Django, Laravel, Spring Boot
APIs: RESTful and GraphQL for connecting front-end with back-end
3. Database Management
Store and retrieve data:
SQL Databases: MySQL, PostgreSQL
NoSQL Databases: MongoDB, CouchDB
4. Version Control and Collaboration
Keep track of changes and work in teams:
Git: Local version control
GitHub/GitLab: Cloud repositories and collaboration
5. Deployment & DevOps Tools
Make your app live and maintain it:
Cloud Platforms: AWS, Azure, Google Cloud
Containerization: Docker
CI/CD Tools: Jenkins, GitHub Actions
Why Full Stack Development is in Demand
With companies increasingly leaning on digital platforms, the demand for professionals who can understand both the client and server sides of development is soaring. Being a full stack web developer means you can:
Build complete web applications independently
Troubleshoot issues across the entire stack
Communicate effectively with both design and backend teams
Offer more value to startups and small businesses
And that’s where training programs like full stack by TechnoBridge come into play.
Learning Full Stack Development with TechnoBridge
If you're planning to start a career in web development or upskill your current profile, full stack by TechnoBridge is a solid place to begin. The program is carefully crafted to guide beginners and intermediates through each layer of full stack web development.
Here’s what you can expect from full stack by TechnoBridge:
Hands-on projects that simulate real-world scenarios
Mentorship from industry experts
Training in both front-end and back-end frameworks
Exposure to DevOps and deployment techniques
Job-oriented sessions with placement support
Such training ensures that you're not just learning to code, but you're learning to build and deliver products that users can interact with seamlessly.
Final Thoughts
As we continue to rely more on digital solutions, full stack developers will remain at the heart of innovation. Whether you’re dreaming of building your own product, working in a startup, or joining a tech giant, understanding the full stack web landscape is your key to staying relevant and competitive.
If you’re looking to dive into this journey, consider programs like full stack by TechnoBridge to gain practical skills, confidence, and a strong professional foundation.
0 notes
Text
Certified DevSecOps Professional: Career Path, Salary & Skills
Introduction
As the demand for secure, agile software development continues to rise, the role of a Certified DevSecOps Professional has become critical in modern IT environments. Organizations today are rapidly adopting DevSecOps to shift security left in the software development lifecycle. This shift means security is no longer an afterthought—it is integrated from the beginning. Whether you're just exploring the DevSecOps tutorial for beginners or looking to level up with a professional certification, understanding the career landscape, salary potential, and required skills can help you plan your next move.
This comprehensive guide explores the journey of becoming a Certified DevSecOps Professional, the skills you'll need, the career opportunities available, and the average salary you can expect. Let’s dive into the practical and professional aspects that make DevSecOps one of the most in-demand IT specialties in 2025 and beyond.
What Is DevSecOps?
Integrating Security into DevOps
DevSecOps is the practice of integrating security into every phase of the DevOps pipeline. Traditional security processes often occur at the end of development, leading to delays and vulnerabilities. DevSecOps introduces security checks early in development, making applications more secure and compliant from the start.
The Goal of DevSecOps
The ultimate goal is to create a culture where development, security, and operations teams collaborate to deliver secure and high-quality software faster. DevSecOps emphasizes automation, continuous integration, continuous delivery (CI/CD), and proactive risk management.
Why Choose a Career as a Certified DevSecOps Professional?
High Demand and Job Security
The need for DevSecOps professionals is growing fast. According to a Cybersecurity Ventures report, there will be 3.5 million unfilled cybersecurity jobs globally by 2025. Many of these roles demand DevSecOps expertise.
Lucrative Salary Packages
Because of the specialized skill set required, DevSecOps professionals are among the highest-paid tech roles. Salaries can range from $110,000 to $180,000 annually depending on experience, location, and industry.
Career Versatility
This role opens up diverse paths such as:
Application Security Engineer
DevSecOps Architect
Cloud Security Engineer
Security Automation Engineer
Roles and Responsibilities of a DevSecOps Professional
Core Responsibilities
Integrate security tools and practices into CI/CD pipelines
Perform threat modeling and vulnerability scanning
Automate compliance and security policies
Conduct security code reviews
Monitor runtime environments for suspicious activities
Collaboration
A Certified DevSecOps Professional acts as a bridge between development, operations, and security teams. Strong communication skills are crucial to ensure secure, efficient, and fast software delivery.
Skills Required to Become a Certified DevSecOps Professional
Technical Skills
Scripting Languages: Bash, Python, or PowerShell
Configuration Management: Ansible, Chef, or Puppet
CI/CD Tools: Jenkins, GitLab CI, CircleCI
Containerization: Docker, Kubernetes
Security Tools: SonarQube, Checkmarx, OWASP ZAP, Aqua Security
Cloud Platforms: AWS, Azure, Google Cloud
Soft Skills
Problem-solving
Collaboration
Communication
Time Management
DevSecOps Tutorial for Beginners: A Step-by-Step Guide
Step 1: Understand the Basics of DevOps
Before diving into DevSecOps, make sure you're clear on DevOps principles, including CI/CD, infrastructure as code, and agile development.
Step 2: Learn Security Fundamentals
Study foundational cybersecurity concepts like threat modeling, encryption, authentication, and access control.
Step 3: Get Hands-On With Tools
Use open-source tools to practice integrating security into DevOps pipelines:
# Example: Running a static analysis scan with SonarQube
sonar-scanner \
-Dsonar.projectKey=myapp \
-Dsonar.sources=. \
-Dsonar.host.url=http://localhost:9000 \
-Dsonar.login=your_token
Step 4: Build Your Own Secure CI/CD Pipeline
Practice creating pipelines with Jenkins or GitLab CI that include steps for:
Static Code Analysis
Dependency Checking
Container Image Scanning
Step 5: Monitor and Respond
Set up tools like Prometheus and Grafana to monitor your applications and detect anomalies.
Certification Paths for DevSecOps
Popular Certifications
Certified DevSecOps Professional
Certified Kubernetes Security Specialist (CKS)
AWS Certified Security - Specialty
GIAC Cloud Security Automation (GCSA)
Exam Topics Typically Include:
Security in CI/CD
Secure Infrastructure as Code
Cloud-native Security Practices
Secure Coding Practices
Salary Outlook for DevSecOps Professionals
Salary by Experience
Entry-Level: $95,000 - $115,000
Mid-Level: $120,000 - $140,000
Senior-Level: $145,000 - $180,000+
Salary by Location
USA: Highest average salaries, especially in tech hubs like San Francisco, Austin, and New York.
India: ₹9 LPA to ₹30+ LPA depending on experience.
Europe: €70,000 - €120,000 depending on country.
Real-World Example: How Companies Use DevSecOps
Case Study: DevSecOps at a Fintech Startup
A fintech company integrated DevSecOps tools like Snyk, Jenkins, and Kubernetes to secure their microservices architecture. They reduced vulnerabilities by 60% in just three months while speeding up deployments by 40%.
Key Takeaways
Early threat detection saves time and cost
Automated pipelines improve consistency and compliance
Developers take ownership of code security
Challenges in DevSecOps and How to Overcome Them
Cultural Resistance
Solution: Conduct training and workshops to foster collaboration between teams.
Tool Integration
Solution: Choose tools that support REST APIs and offer strong documentation.
Skill Gaps
Solution: Continuous learning and upskilling through real-world projects and sandbox environments.
Career Roadmap: From Beginner to Expert
Beginner Level
Understand DevSecOps concepts
Explore basic tools and scripting
Start with a DevSecOps tutorial for beginners
Intermediate Level
Build and manage secure CI/CD pipelines
Gain practical experience with container security and cloud security
Advanced Level
Architect secure cloud infrastructure
Lead DevSecOps adoption in organizations
Mentor junior engineers
Conclusion
The future of software development is secure, agile, and automated—and that means DevSecOps. Becoming a Certified DevSecOps Professional offers not only job security and high salaries but also the chance to play a vital role in creating safer digital ecosystems. Whether you’re following a DevSecOps tutorial for beginners or advancing into certification prep, this career path is both rewarding and future-proof.
Take the first step today: Start learning, start practicing, and aim for certification!
1 note
·
View note
Text
Cloud Computing for Programmers

Cloud computing has revolutionized how software is built, deployed, and scaled. As a programmer, understanding cloud services and infrastructure is essential to creating efficient, modern applications. In this guide, we’ll explore the basics and benefits of cloud computing for developers.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing allows you to access computing resources (servers, databases, storage, etc.) over the internet instead of owning physical hardware. Major cloud providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
Key Cloud Computing Models
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service): Provides virtual servers, storage, and networking (e.g., AWS EC2, Azure VMs)
PaaS (Platform as a Service): Offers tools and frameworks to build applications without managing servers (e.g., Heroku, Google App Engine)
SaaS (Software as a Service): Cloud-hosted apps accessible via browser (e.g., Gmail, Dropbox)
Why Programmers Should Learn Cloud
Deploy apps quickly and globally
Scale applications with demand
Use managed databases and storage
Integrate with AI, ML, and big data tools
Automate infrastructure with DevOps tools
Popular Cloud Services for Developers
AWS: EC2, Lambda, S3, RDS, DynamoDB
Azure: App Services, Functions, Cosmos DB, Blob Storage
Google Cloud: Compute Engine, Cloud Run, Firebase, BigQuery
Common Use Cases
Hosting web and mobile applications
Serverless computing for microservices
Real-time data analytics and dashboards
Cloud-based CI/CD pipelines
Machine learning model deployment
Getting Started with the Cloud
Create an account with a cloud provider (AWS, Azure, GCP)
Start with a free tier or sandbox environment
Launch your first VM or web app
Use the provider’s CLI or SDK to deploy code
Monitor usage and set up billing alerts
Example: Deploying a Node.js App on Heroku (PaaS)
# Step 1: Install Heroku CLI heroku login # Step 2: Create a new Heroku app heroku create my-node-app # Step 3: Deploy your code git push heroku main # Step 4: Open your app heroku open
Tools and Frameworks
Docker: Containerize your apps for portability
Kubernetes: Orchestrate containers at scale
Terraform: Automate cloud infrastructure with code
CI/CD tools: GitHub Actions, Jenkins, GitLab CI
Security Best Practices
Use IAM roles and permissions
Encrypt data at rest and in transit
Enable firewalls and VPCs
Regularly update dependencies and monitor threats
Conclusion
Cloud computing enables developers to build powerful, scalable, and reliable software with ease. Whether you’re developing web apps, APIs, or machine learning services, cloud platforms provide the tools you need to succeed in today’s tech-driven world.
0 notes
Text
Bridging the Gap: A Developer's Roadmap to Embracing DevOps Excellence
In the ever-evolving landscape of software development, the role of a DevOps engineer stands out as a crucial link between development and operations. For developers with an eye on this transformative career path, acquiring a unique skill set and embracing a holistic mindset becomes imperative. In the city of Hyderabad, DevOps Training offers a strategic avenue for individuals keen on validating their proficiency in DevOps practices and enhancing their career trajectory.

Charting the DevOps Odyssey: A Developer's Comprehensive Guide
Shifting gears from a developer to a DevOps engineer involves a nuanced approach, harmonizing development expertise with operational acumen. Here's a detailed step-by-step guide to assist developers aspiring to embark on the dynamic journey into the world of DevOps:
1. Grasp the Fundamentals of DevOps: Establish a solid foundation by delving into the core principles of DevOps, emphasizing collaboration, automation, and a culture of continuous improvement. Recognize the significance of the cultural shift required for successful DevOps implementation.
2. Master Git and Version Control: Dive into the world of version control with a mastery of Git, including branches and pull requests. Proficiency in these areas is pivotal for streamlined code collaboration, versioning, and effective tracking of changes.
3. Cultivate Scripting Skills (e.g., Python, Shell): Cultivate essential scripting skills to automate mundane tasks. Languages like Python and Shell scripting play a key role in the DevOps toolchain, providing a robust foundation for automation.
4. Explore Containers and Kubernetes: Immerse yourself in the realms of containerization with Docker and orchestration with Kubernetes. A comprehensive understanding of these technologies is fundamental for creating reproducible environments and managing scalable applications.
5. Grasp Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Familiarize yourself with Infrastructure as Code (IaC) principles. Tools like Terraform or Ansible empower the codification of infrastructure, streamlining deployment processes. The pursuit of the Best DevOps Online Training can offer profound insights into leveraging IaC effectively.

6. Experiment with Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD): Take the leap into CI/CD territory with experimentation using tools like Jenkins or GitLab CI. The automation of code testing, integration, and deployment is pivotal for ensuring swift and reliable releases within the development pipeline.
7. Explore Monitoring and Logging: Gain proficiency in monitoring and troubleshooting by exploring tools like Prometheus or Grafana. A deep understanding of the health and performance of applications is crucial for maintaining a robust system.
8. Foster Collaboration with Other Teams: Cultivate effective communication and collaboration with operations, QA, and security teams. DevOps thrives on breaking down silos and fostering a collaborative environment to achieve shared goals.
Remember, the transition to a DevOps role is an evolutionary process, where gradual incorporation of DevOps practices into existing roles, coupled with hands-on projects, fortifies the foundation for a successful journey towards becoming a DevOps engineer.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Unlocking Creativity and Efficiency with Development Tools Software
Development tools software is the backbone of modern software creation, empowering developers to design, build, test, and deploy applications with precision and speed. From writing code to debugging errors and managing projects, these tools streamline every stage of the development process, making them essential for programmers, businesses, and tech innovators. But what exactly is development tools software, how does it work, and why is it so vital in today’s tech-driven world? In this guide, we’ll explore its fundamentals, types, benefits, and tips for choosing the right tools, followed by an FAQ to address common questions.

What Is Development Tools Software?
Development tools software refers to a suite of applications, frameworks, and utilities designed to assist developers in creating software, websites, or apps. These tools cover a wide range of tasks: writing and editing code (e.g., Visual Studio Code), debugging (e.g., Chrome DevTools), version control (e.g., Git), and automating builds (e.g., Jenkins). They can be standalone programs or integrated into larger platforms called Integrated Development Environments (IDEs), which combine multiple tools into a single interface.
At its essence, development tools software enhances productivity by automating repetitive tasks, catching errors early, and providing a structured environment for coding. Whether you’re building a mobile game, a web app, or an enterprise system, these tools are the craftsman’s kit for turning ideas into functional software.
How Does Development Tools Software Work?
Development tools software operates by providing specialized functionalities tailored to the software development lifecycle:
Coding: Editors like Sublime Text or IDEs like IntelliJ IDEA offer syntax highlighting, auto-completion, and code suggestions.
Debugging: Tools like GDB or built-in IDE debuggers identify and fix bugs by stepping through code execution.
Testing: Frameworks like JUnit or Selenium automate testing to ensure code reliability.
Collaboration: Version control systems like Git (via GitHub or GitLab) track changes and enable team workflows.
Deployment: Build tools like Maven or CI/CD platforms like CircleCI compile and release software to production.
For example, a developer might use Visual Studio Code to write Python, debug it with PyCharm’s tools, test it with pytest, and push it to GitHub—all powered by different development tools software working in harmony.
Types of Development Tools Software
The category is broad, with tools specializing in various development stages:
Code Editors: Lightweight tools like VS Code or Atom for writing and editing code.
Integrated Development Environments (IDEs): All-in-one platforms like Eclipse or Xcode, combining editing, debugging, and more.
Version Control Systems: Git, Subversion (SVN), or Mercurial for tracking code changes.
Build Tools: Maven, Gradle, or npm for automating compilation and dependency management.
Testing Tools: Jest, Mocha, or Postman for validating functionality and APIs.
CI/CD Tools: Jenkins, Travis CI, or GitHub Actions for continuous integration and deployment.
Each type addresses a specific need, often used together for a seamless workflow.
Applications of Development Tools Software
Development tools software powers a vast array of projects:
Web Development: Tools like VS Code and Webpack build responsive sites.
Mobile Apps: Android Studio or Flutter create apps for iOS and Android.
Game Development: Unity and Unreal Engine craft immersive games.
Enterprise Software: IntelliJ IDEA and Jenkins support complex business systems.
Open-Source Projects: Git and GitHub enable global collaboration.
AI/ML: Jupyter Notebook and TensorFlow aid machine learning development.
These tools are the foundation for innovation across industries, from startups to tech giants.
Benefits of Development Tools Software
Productivity: Automates repetitive tasks, letting developers focus on logic and creativity.
Accuracy: Debugging and testing tools catch errors before they reach users.
Collaboration: Version control fosters teamwork on shared codebases.
Scalability: Build and CI/CD tools handle projects from small scripts to massive systems.
Learning Curve: Modern tools often include tutorials and community support, easing onboarding.
Popular Development Tools Software Options
Visual Studio Code: A free, extensible code editor with broad language support.
IntelliJ IDEA: A powerful IDE for Java and beyond, with smart code assistance.
Git: The leading version control system, paired with platforms like GitHub.
Jenkins: An open-source CI/CD tool for automating builds and deployments.
Postman: A go-to for API testing and development.
Unity: A game development engine with robust tools for 2D and 3D projects.
These range from free, community-driven options to premium, enterprise-grade solutions.
How to Choose the Right Development Tools Software
Selecting the best tools depends on your needs:
Project Type: Web devs might pick VS Code; game devs might choose Unity.
Language: Ensure compatibility—e.g., PyCharm for Python, Xcode for Swift.
Skill Level: Beginners favor simple editors; pros might use full IDEs.
Budget: Free tools like Git suit tight budgets; paid IDEs like IntelliJ offer advanced features.
Community: Tools with active forums (e.g., VS Code) provide better support.
Experimenting with free versions or open-source options can guide your decision.
The Future of Development Tools Software
The landscape is evolving with trends like:
AI Assistance: Tools like GitHub Copilot suggest code in real time.
Cloud Integration: IDEs like Gitpod run entirely in the browser.
Low-Code Platforms: Simplifying development for non-coders.
Collaboration: Real-time coding tools like Replit enhance teamwork.
As software grows more complex, development tools will become smarter and more accessible.
Conclusion
Development tools software is the engine driving software creation, offering developers the power to build efficiently, collaboratively, and innovatively. Whether you’re a hobbyist coding a side project or a team launching a global app, these tools are your allies in turning vision into reality. By understanding their types and benefits, you can pick the perfect toolkit to elevate your development journey.
FAQ: Development Tools Software
What is development tools software? A: It’s software that helps developers write, test, debug, and deploy code, including editors, IDEs, and version control systems.
How does it differ from regular software? A: Regular software is for end-users; development tools software is for creating that software.
What are the main types of development tools software? A: Code editors (VS Code), IDEs (IntelliJ), version control (Git), build tools (Maven), testing tools (Jest), and CI/CD (Jenkins).
Who uses development tools software? A: Programmers, web developers, app creators, game designers, and tech teams rely on it.
Do I need coding skills to use development tools software? A: Basic tools like VS Code need minimal coding knowledge, but advanced ones like Jenkins require expertise.
Is development tools software free? A: Many are—like Git and VS Code—though premium tools (e.g., IntelliJ Ultimate, $499/year) offer extra features.
Can I use development tools software offline? A: Yes, editors and IDEs often work offline, but cloud-based or collaboration tools need internet.
What’s the best development tools software for beginners? A: VS Code is lightweight and beginner-friendly, with plenty of tutorials and extensions.
How do development tools improve productivity? A: They automate tasks, catch errors early, and streamline workflows, saving time and effort.
What’s the future of development tools software? A: Expect more AI-driven coding aids, cloud-based IDEs, and tools for non-coders as the field evolves.
0 notes
Text
How to Hire DevSecOps Developers: A Step-by-Step Guide

Cybersecurity has become a paramount concern for the majority of the businesses and is a top priority in the majority of the development processes. The demand for DevSecOps developers has outgrown because they embed security in every stage of the software development lifecycle to reduce risks and improve overall system resilience.
Data protection and uptime are vital for your SaaS business which is why you need to have a skilled DevSecOps team for ensuring security, scalability, and compliant applications. For this let’s understand what are the right skills, hiring process, and recruitment strategies you must consider when you hire software engineers for this purpose.
A Step-by-Step Hiring Guide to Building a Strong and Secure DevSecOps Team
State your hiring requirements
List the primary duties and competencies that your DevSecOps developer must possess before you begin your search. Take into account:
Proficiency in cloud security - familiarity with AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud.
Knowledge of automation and CI/CD: familiarity with Kubernetes, Jenkins, and GitLab CI/CD.
Comprehending security frameworks like NIST, SOC 2, and GDPR is essential for threat modelling and security compliance.
The hiring process is streamlined and the right talent is drawn in when these requirements are clearly stated.
Use reputed platforms to source talent
Although it can be difficult to find great talent, the following platforms can help:
Job portals: Indeed, Glassdoor, and LinkedIn for full-time roles; freelance platforms: Upwork and Toptal for contract-based recruiting.
IT staffing agencies: specialized companies that offer talent that is ready for employment after pre-screening applicants. Uplers is a hiring platform that unlike IT staffing agencies provides you AI-vetted top talent from India in a 4-step process.
Without having to spend months on hiring, SaaS organizations can discover skilled DevSecOps developers more rapidly by collaborating with such hiring platforms.
Screen and evaluate candidates
Make sure you carry out comprehensive evaluations to ensure you recruit the top talent:
Technical interviews: Assess their familiarity with cloud security best practices and DevSecOps tools.
Practical exercises: Evaluate their proficiency in automating security checks in CI/CD pipelines.
Assessment of soft skills: Verify excellent problem-solving and teamwork capabilities.
Long-term success for SaaS organizations depends on hiring DevSecOps developers who can comprehend the challenges of protecting cloud-based apps.
Offer competitive compensation and benefits
Offering competitive pay and benefits is crucial given the growing demand for DevSecOps expertise. Take into account:
Flexibility in remote work: Many DevSecOps engineers choose remote positions.
Opportunities for continuous learning: Discuss certifications and training such as CISSP or AWS Security.
Alluring benefits packages: Offering competitive pay helps you retain top developers.
Hiring software engineers that can work with DevSecOps experts on secure coding techniques may also be necessary if you require more backend help. You could also use free tools like the Uplers salary benchmarking tool to compare, contrast, and adjust your compensation offering with the industry standards.
Onboarding and retention strategies
Long-term success is ensured by a seamless onboarding process for DevSecOps developers:
Establish clear security policies and workflows to incorporate them into your team.
Assign mentors to assist them in understanding internal security procedures.
Promote ongoing development via security research and training.
Retaining top security staff lowers risks, improves compliance, and increases system resilience for SaaS organizations.
Summing Up
Integrating security into your software development process requires hiring the best DevSecOps developers. You may create a robust DevSecOps team by establishing clear requirements, using IT staffing companies, and carrying out in-depth assessments.
Investing in qualified experts guarantees long-term security and efficiency. Having a proactive security plan is essential for SaaS organizations; and no longer a choice.
0 notes
Text
Understanding CI/CD Pipelines: Automating Your Workflow

Introduction
Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Deployment (CD) have become essential in modern software development. They automate the software release process, allowing teams to build, test, and deploy applications efficiently.
In this guide, we’ll explore the concepts, benefits, and steps involved in setting up a CI/CD pipeline.
1. What is CI/CD?
Continuous Integration (CI)
CI is the practice of frequently merging code changes into a shared repository. Each change triggers an automated build and test process to detect bugs early.
Key Benefits: ✅ Faster bug detection ✅ Improved collaboration ✅ Reduced integration issues
Continuous Deployment (CD)
CD ensures that changes passing CI tests are automatically deployed to production or staging environments.
Key Benefits: ✅ Faster release cycles ✅ Reduced manual errors ✅ Increased reliability
2. How Does a CI/CD Pipeline Work?
A typical CI/CD pipeline consists of the following stages:
Code Commit — Developers push changes to a version control system (e.g., GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket).
Build Stage — The code is compiled and dependencies are installed.
Testing Stage — Automated tests (unit, integration, security tests) run to ensure functionality.
Deployment Stage — If tests pass, the application is deployed to staging or production.
Monitoring & Feedback — Logs and performance metrics help identify issues.
3. Popular CI/CD Tools
🚀 Jenkins — Open-source automation server 🚀 GitHub Actions — Integrated with GitHub repositories 🚀 GitLab CI/CD — Built-in CI/CD for GitLab 🚀 CircleCI — Cloud-based CI/CD tool 🚀 Travis CI — Easy-to-configure CI/CD service 🚀 AWS Code Pipeline — CI/CD for AWS environments
4. Setting Up a Basic CI/CD Pipeline with GitHub Actions
Step 1: Create a .github/workflows/ci-cd-pipeline.yml File
yamlname: CI/CD Pipelineon: push: branches: - mainjobs: build: runs-on: ubuntu-latest steps: - name: Checkout code uses: actions/checkout@v2 - name: Install dependencies run: npm install - name: Run tests run: npm test - name: Deploy to production run: echo "Deploying..."
5. Best Practices for CI/CD
✔️ Automate Everything — Build, test, and deploy automatically. ✔️ Use Feature Flags — Control feature rollouts safely. ✔️ Monitor Deployments — Use logs and analytics to detect issues. ✔️ Implement Security Scans — Prevent vulnerabilities before deployment. ✔️ Rollback Strategies — Prepare for quick rollbacks in case of failure.
Conclusion
CI/CD pipelines streamline development, improve code quality, and accelerate releases. By integrating automation, testing, and deployment, teams can deliver robust applications efficiently.
WEBSITE: https://www.ficusoft.in/full-stack-developer-course-in-chennai/
0 notes